Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine or cervical osteochondrosis is a disease of degenerative-dystrophic genesis that affects the intervertebral discs and cervical vertebrae with the formation of protrusions and intervertebral hernias, which ultimately leads to spinal cord dysfunction and is often the cause of the patient's spinal cord. damage.
Characteristics of the structure of the cervical spine
The vertebrae are the bones that make up the spine. Each vertebra has a body that carries the entire load, the vertebral arch, the transverse and spinous processes.
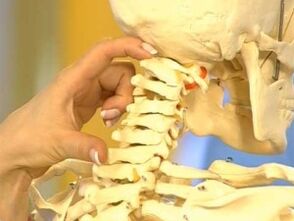
The vertebral arches of the vertebrae form the spinal canal through which the spinal cord passes. The processes of the spine are designed to anchor the muscles of the back.
There are also anterior and posterior connections that connect the vertebrae together.
The intervertebral disc is a rounded flat structure that consists of a fibrous ring and a pulpal nucleus, whose main function is shock absorption. The intervertebral discs are located between the vertebrae.
The facet joint is a movable connection of the growths of two adjacent vertebrae. Facet joints provide flexibility to the spine.
Intervertebral foramina are openings that are formed by structural elements (legs, articular processes) of two adjacent vertebrae and are designed for the exit of the radicular nerves of the spinal cord.
There are paravertebral muscles that support the spine and its various movements.
The cervical vertebra is the uppermost and most mobile part of the spine, which consists of seven vertebrae and has a C-shape due to its forward curvature (cervical lordosis).
All movements of the head - tilt, rotation, circular, are provided by this part of the spine.
Interesting! In addition, the cervical vertebra is the most traumatized part, as the cervical vertebrae have low strength and a weak muscular apparatus compared to others.
For the same reason, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine often occurs.
Prevalence of cervical osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine affects the working age population over 30 years. This disease is more common in women than in men.
According to the World Health Organization, 40-90% of the world's population suffers from osteochondrosis.
Important!Every second patient with osteochondrosis has dystrophic and degenerative changes in the spine in the cervical spine.
Causes of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Osteochondrosis can be called a tribute to a person's ability to stand and walk on two legs. This view is confirmed by the fact that no animal that walks on all fours suffers from osteochondrosis.
Despite the availability of modern methods for diagnosing diseases and in-depth knowledge of human anatomy and physiology, it is still not possible to establish the specific causes of osteochondrosis.

But reliable factors are known that lead to degenerative-dystrophic changes in the spine. These include the following:
- insufficient mobile lifestyle of a person, which leads to weakening of the muscular apparatus of the back. Often office workers, cashiers, salespeople and drivers suffer from osteochondrosis;
- heavy physical work;
- mechanical back injury;
- genetic predisposition to osteochondrosis;
- overweight and obesity;
- neuropsychiatric stress;
- improper workouts in the gym;
- beriberi, micronutrient deficiency, metabolic disorders;
- malnutrition;
- the presence of diseases of the kidneys, digestive and endocrine systems;
- infectious diseases;
- frequent hypothermia of the body;
- congenital and acquired immunodeficiencies.
Pathogenesis (mechanism of development) of cervical osteochondrosis

Almost all factors contributing to the development of osteochondrosis lead to spasm of the back muscles. In turn, muscle spasm disrupts the blood supply and metabolism of the bone tissue of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
In this way, dystrophic changes occur, in other words, dehydration, dehydration and loss of elasticity of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs.
Further loading of the spine leads to flattening, protrusion (protrusion outside the fibrous ring) of the intervertebral discs.
No less important in the pathogenesis of cervical osteochondrosis is the load of retention and movement of the head.
The load on the cervical vertebrae is huge, as the average weight of the head is 3-5 kg, and their bone tissue, unfortunately, is fragile and thin.
Also, the development of osteochondrosis is facilitated by technical progress - smartphones, tablets, e-books, if you bend over while using these devices.
The intervertebral discs cannot effectively perform damping of the spine, which is why compensatory mechanisms are activated.
Important!One of these mechanisms is the proliferation of osteophytes and the development of spondylosis.
False joints - uncovertebral arthrosis - can also form on the posterior surface of the cervical vertebrae.
All these processes eventually lead to a reduction in cervical lordosis (hypolordosis), bulges and intervertebral discs, which sooner or later become the main cause of injury or require urgent surgical treatment.
The pathogenesis of cervical osteochondrosis can be divided into four stages:
- The onset of instability of the cervical spine;
- The formation of a protrusion of the intervertebral discs, reduction of the intervertebral fissure, the beginning of the destruction of the fibrous ring, which leads to pinching of the nerves, which is manifested by pain in the neck;
- The fibrous ring is completely destroyed and the pulpal nucleus extends beyond its boundaries, thus forming an intervertebral hernia and deforming the spine;
- Stage of damage. The vertebrae grow together. It is difficult for patients to move. Sometimes the condition can improve, but not for long.
Symptoms and syndromes of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
The main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis include the following:
- persistent neck pain of a throbbing or painful nature that may spread to the occipital region of the head, eye sockets, ears, and shoulder girdle;
- pain in the upper extremities, which increases with movement;
- stiffness of the movements of the upper limbs, violation of their sensitivity (tingling, burning, tingling), weakening of muscle strength;
- morning stiffness in the neck;
- soreness in the cervical spine when moving the head;
- periodic dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis, darkening of the eyes, loss of consciousness with sharp turns of the head;
- sensation of tinnitus;
- hearing and vision impairment;
- tingling and numbness of the tongue;
- cardialgia (heart pain), sometimes cervical osteochondrosis is confused with acute coronary syndrome. The difference is the lack of effect of nitrates;
- due to microcirculation disorders and lack of tissue oxygen, connective tissue multiplies in the cervical spine, the so-called "living room".
All symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis can be grouped into the following syndromes:
- reflex;
- radicular;
- radicular-vascular;
- compression of the spine;
- cerebral.
The reflex syndrome consists of cervicalgia - intense pain in the neck, due to which the patient is forced to fixate the head and tense the muscles of the neck.
The sensation of spinous growths, paravertebral points and intervertebral discs carries and / or intensifies the pain.
Also, the reflex syndrome is characterized by pain in the upper limbs, occipital or temporal area of the head.
Radicular syndrome is a combination of acute sharp pain that is exacerbated by head movements and arises from pinching nerves in the intervertebral foramen.
Radicular-vascular syndrome is characterized by vegetative-trophic disorders in the form of shoulder-scapular periarthritis.
The patient is worried about pain in the shoulder joint, stiffness of movements, impaired skin sensitivity, swelling of the arm and wrist. In addition, the patient cannot return his hands.
Spinal compression syndrome occurs due to compression of the spinal cord and its vascular apparatus. Disc herniation, osteophytes, thickening of the yellow ligament can lead to this.
Interesting!Patients have pain in the neck and shoulder area, relaxed paresis of the upper extremities and spastic paresis of the lower extremities, impaired sensitivity.
Cerebral syndrome with cervical osteochondrosis combines several such syndromes:
- diencephalic syndrome - increased irritability, neurasthenia, general weakness, insomnia, distraction. In severe cases, there is anxiety, tingling in the upper and lower extremities, increased sweating, chills;
- posterior cervical sympathetic Barre's syndrome or "cervical migraine" - intense headaches, as in migraine in one half of the head on the background of dizziness, visual and auditory impairment, tingling sensation in the hands.
- syncope syndrome - seizure with a sharp turn of the head;
- vestibular-stem and cochlear-stem syndromes - dizziness, instability when walking, nausea and even vomiting;
- syndrome of visual disturbances - deterioration of vision, visual disturbances, blinking of "dots", "flies" in front of the eyes.
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
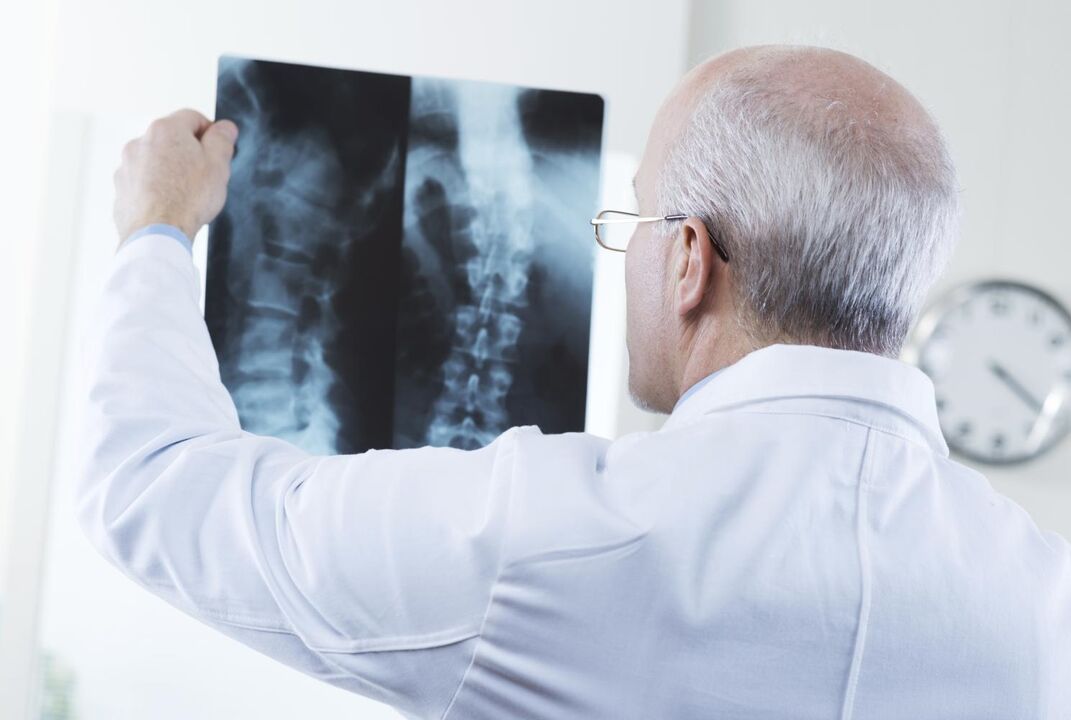
Like any diagnosis in medicine, the diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is made on the basis of the patient's complaints, medical history, examination and auxiliary examination methods.
In addition to the clinical examination, the patient should undergo the following methods:
- X-ray of the cervical spine;
- Computed tomography of the cervical spine;
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the cervical spine;
- Doppler ultrasound examination of the vessels of the neck;
After the diagnostic measures, the doctor chooses the tactics of treatment based on the results of the diagnosis and analysis.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
The treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine consists in eliminating the radicular syndrome and eliminating the inflammatory process.

In the acute period of the disease you should adhere to strict bed rest. The soft mattress should be replaced with a hard one or a wooden shield should be placed on it.
Drug therapy for cervical osteochondrosis is performed using the following groups of drugs:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- drugs from the chondroprotective group;
- analgesic and anti-inflammatory gels and ointments;
- vitamin preparations - ascorbic acid, retinol acetate, tocopherol acetate;
- calcium preparations;
- drugs that improve tissue microcirculation;
- muscle relaxants.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis includes the following methods:
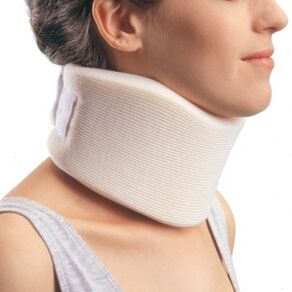
- wearing a special collar around the neck, which not only relieves the load from the neck, but also restricts movement;
- stretching with a Gleason loop - the patient's head lying on the bed is fixed with a Gleason loop, and the head of the bed is raised by 20-30 cm. This procedure relaxes the muscular corset of the spine, increases intervertebral fissures, releases pinched nerves;
- manual therapy for cervical osteochondrosis should only be performed by an experienced chiropractor. Manual therapy is performed with the help of techniques for relaxing and segmental massage, mobilization, which restores the damaged joint functions, and manipulations to restore the full amplitude of movement in the joints.
- physiotherapeutic methods for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine - diadynamotherapy, electrotherapy, laser therapy, shock wave therapy, balneotherapy, treatment with ultrasound and ultraviolet rays, magnetic therapy and other methods.
- Physiotherapy for cervical osteochondrosis includes exercises to strengthen the muscular corset. Exercise is suitable not only for the treatment of osteochondrosis, but also for prevention. They can be done before bed at home, in the gym, at work and at school during the holidays.
Surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis
Surgical treatment is indicated for severe radicular syndrome, which cannot be relieved with medication, with increased impaired motor and sensory functions of the upper extremities, as well as for compression of the spinal cord.
Important!Surgery to remove intervertebral disc herniation and osteophytes is widely used.
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine

- healthy sleep on an orthopedic mattress;
- use of a low pillow;
- visit the sauna or bath regularly. The steam perfectly relaxes the neck muscles;
- you should take a hot shower every day for at least 10 minutes;
- to do sports, gymnastics, walking. Swimming, yoga, Pilates are great for this;
- all head movements must be precise, without sharp turns;
- properly distribute the load on the spine during physical labor and sports;
- take breaks and warm up during sedentary work;
- maintain proper posture while sitting at a table or computer;
- the chairs and the table should be suitable for your height.



















